A web server for scaffolding contigs using multiple reference genomes
A web server for scaffolding contigs using multiple reference genomes
The Multi-CSAR web server is a multiple reference-based scaffolder that can efficiently produce more accurate scaffolds of a target draft genome by referring to multiple complete and/or incomplete genomes of related organisms.
Multi-CSAR provides a web interface (see Figure 1 for an example) that is intuitive and easy to operate. For convenience, the users can choose one of the examples (1) we prepared in advance for testing or running Multi-CSAR, or submit a job according to the following procedures.
The users can click the "Help" tab page (11) to view a brief instruction on how to run Multi-CSAR.
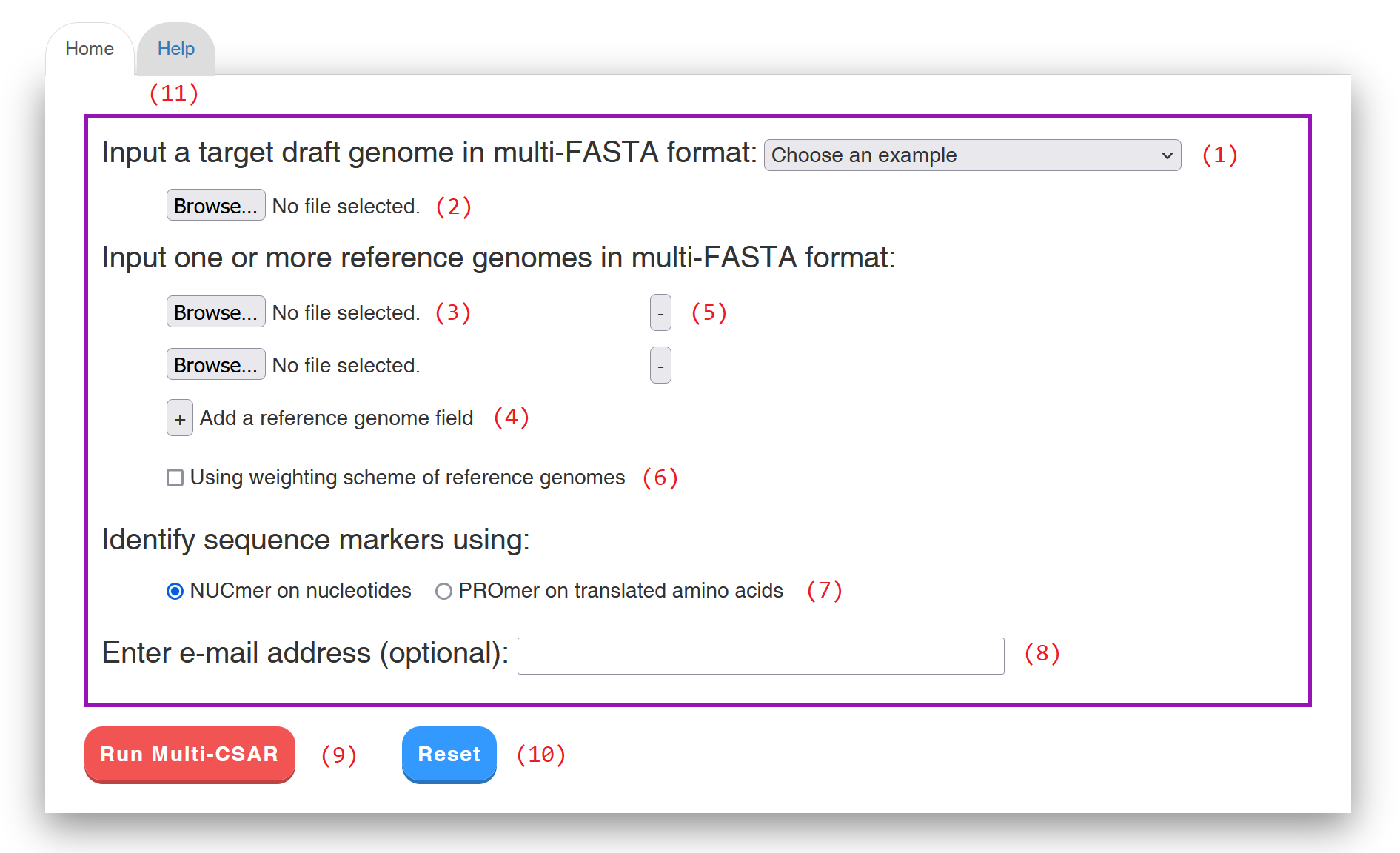
Figure 1: Web interface of Multi-CSAR.
Multi-CSAR outputs its scaffolding results in four tab pages: (1) input data & parameters, (2) Circos plot validation, (3) dotplot validation, and (4) scaffolds of target.
In the "Input data & parameters" tab page (see Figure 2 for an example), Multi-CSAR shows the sequence information of input target and reference genomes, the user-specified sequence aligner (either NUCmer or PROmer) to identify their sequence markers (i.e., similar genomic segments), and whether the weighting scheme of reference genomes is used or not. By clicking on the links of the target and reference genomes, Multi-CSAR will display their input DNA sequences, which can be downloaded by the users when further clicking on "Download sequence" button. By clicking on the link "Dotplot against target genome", Multi-CSAR will display a dotplot, which allows the users to visually inspect sequence markers shared between un-scaffolded target genome and a selected reference genome. In the dotplot (see Figure 3 for an example), the un-scaffolded target genome and the selected reference genome are plotted on the y and x axes, respectively, where their contigs and/or scaffolds are separated by horizontal or vertical dashed lines. In addition, forward and reverse sequence markers are displayed in red and blue lines, respectively, where the beginning and end of each line are represented by two unfilled points. The users have an option to sort the input contigs of the target genome according to their sizes by using the toggle switch "Sort by contig size". In addition, the users can show or hide the IDs of contigs and scaffolds used in Multi-CSAR by clicking on the toggle switch "Show contig/scaffold IDs". The format of contig (respectively, scaffold) IDs begins with three-letter prefix CTG (respectively, SCF) followed by an underscore (_) and at least one digit (e.g., CTG_1 and SCF_1). The users can further view the IDs used in Multi-CSAR to denote the scaffolds of each reference genome by clicking on the link "Scaffold IDs".
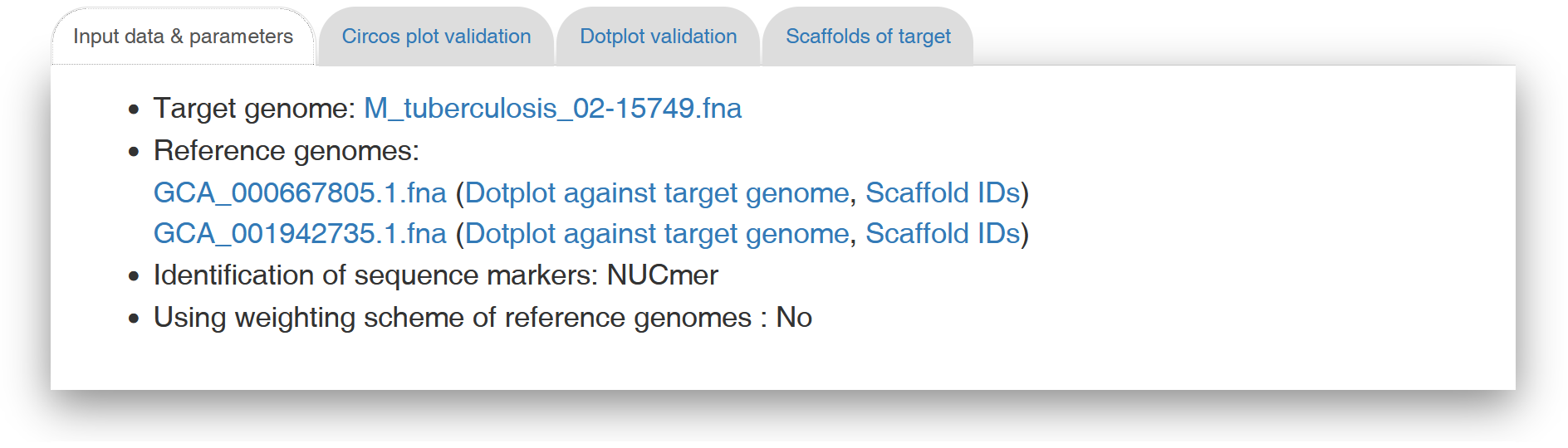
Figure 2: A display of the "Input data & parameters" tab page.
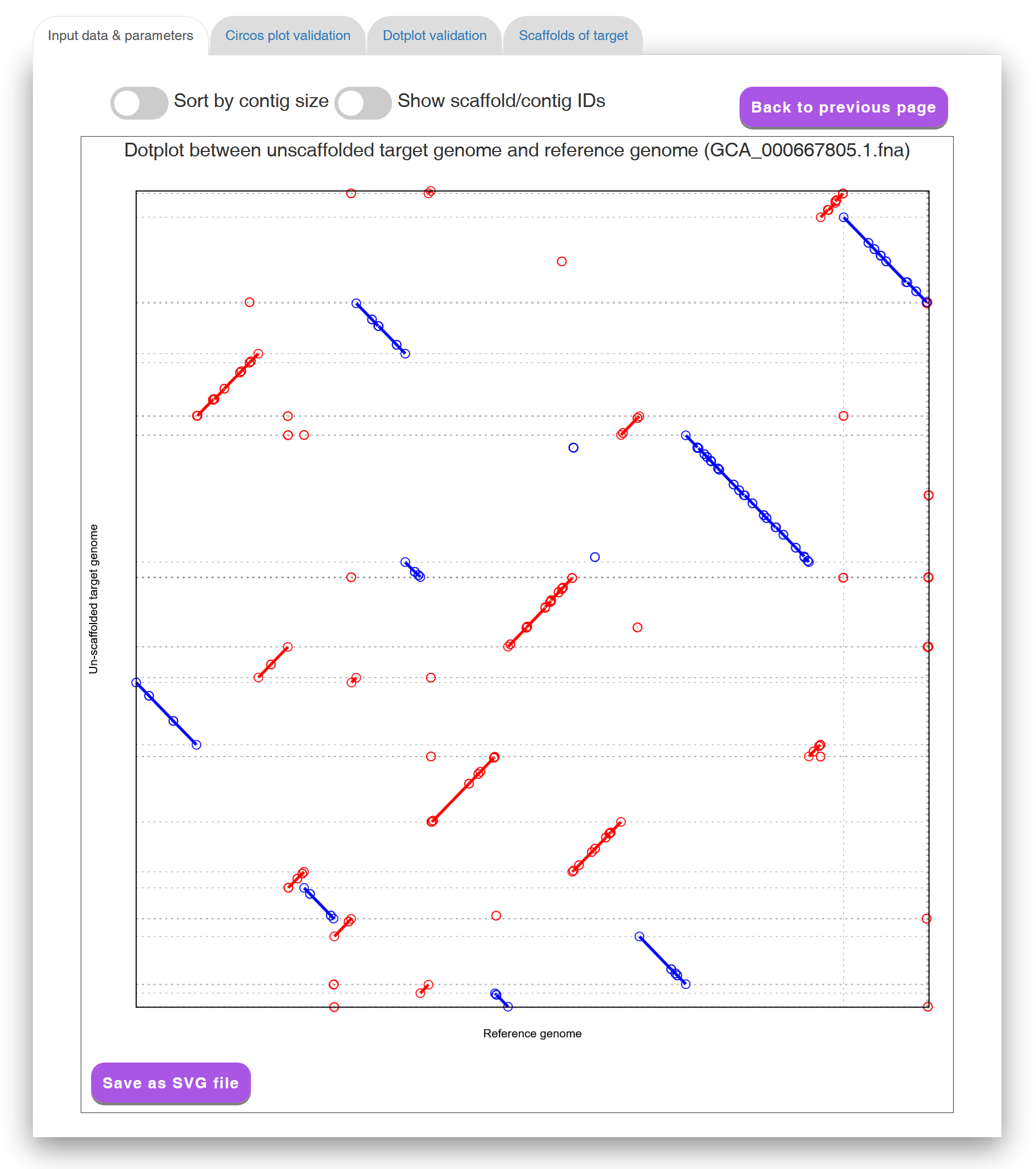
Figure 3: A display of a dotplot between un-scaffolded target genome
and a reference genome.
In the "Circos plot validation" tab page (see Figure 4 for an example), Multi-CSAR displays its total running time, as well as its scaffolding result by a Circos plot between scaffolded target genome and all reference genomes. In the initial Circos plot, the scaffolds of target genome (displayed in purple) and all the reference genomes (displayed in other colors) are arranged in a circle with the inner links connecting corresponding sequence markers between the target genome and each of reference genomes. The color of an inner link comes from the reference it connects. In the Circos plot, the number of crossing inner links can be viewed as a accuracy measure for a scaffolding result. That is, if the contigs of the target genome are scaffolded well according to a reference genome, the number of crossing inner links between them should be low. For this purpose, Multi-CSAR allows the users to select any reference genome (by clicking the checkbox next to it) from the top of the tab page to display (by clicking the "Display Circos plot" button) its Circos plot against the scaffolded target genome (see Figure 5 for an example). In this Circos plot, the inner circle displays the sequence markers shared between the target genome and the selected reference genome. As demonstrated above, the Circos plots of the scaffolding result are convenient and helpful for the users to visually validate whether the contigs of the target genome are properly scaffolded according to the reference genomes, as well as to visually identify whether there are any genome rearrangements between the scaffolded target and reference genomes.
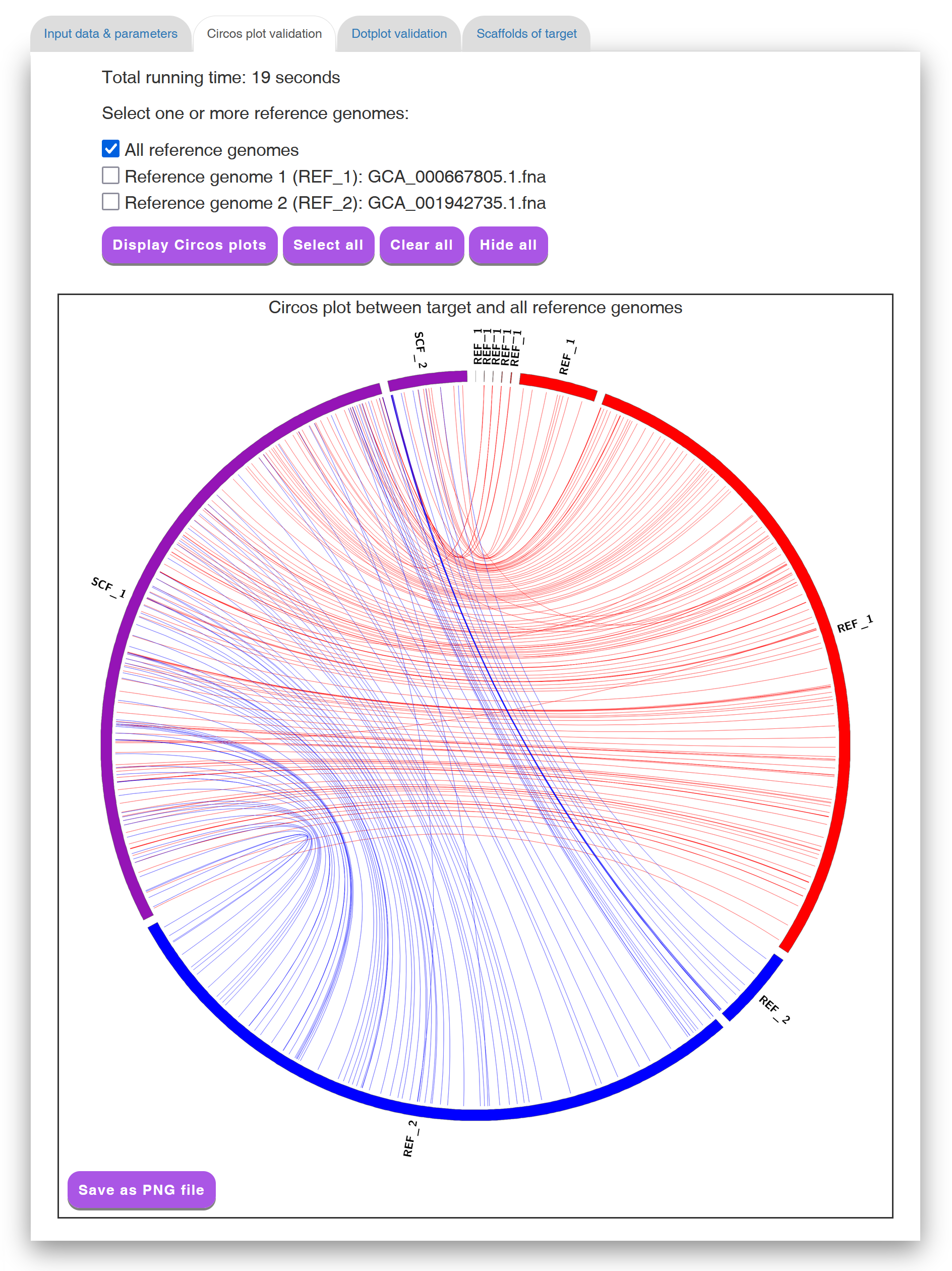
Figure 4: A display of a Circos plot between scaffolded target genome
and all reference genomes.
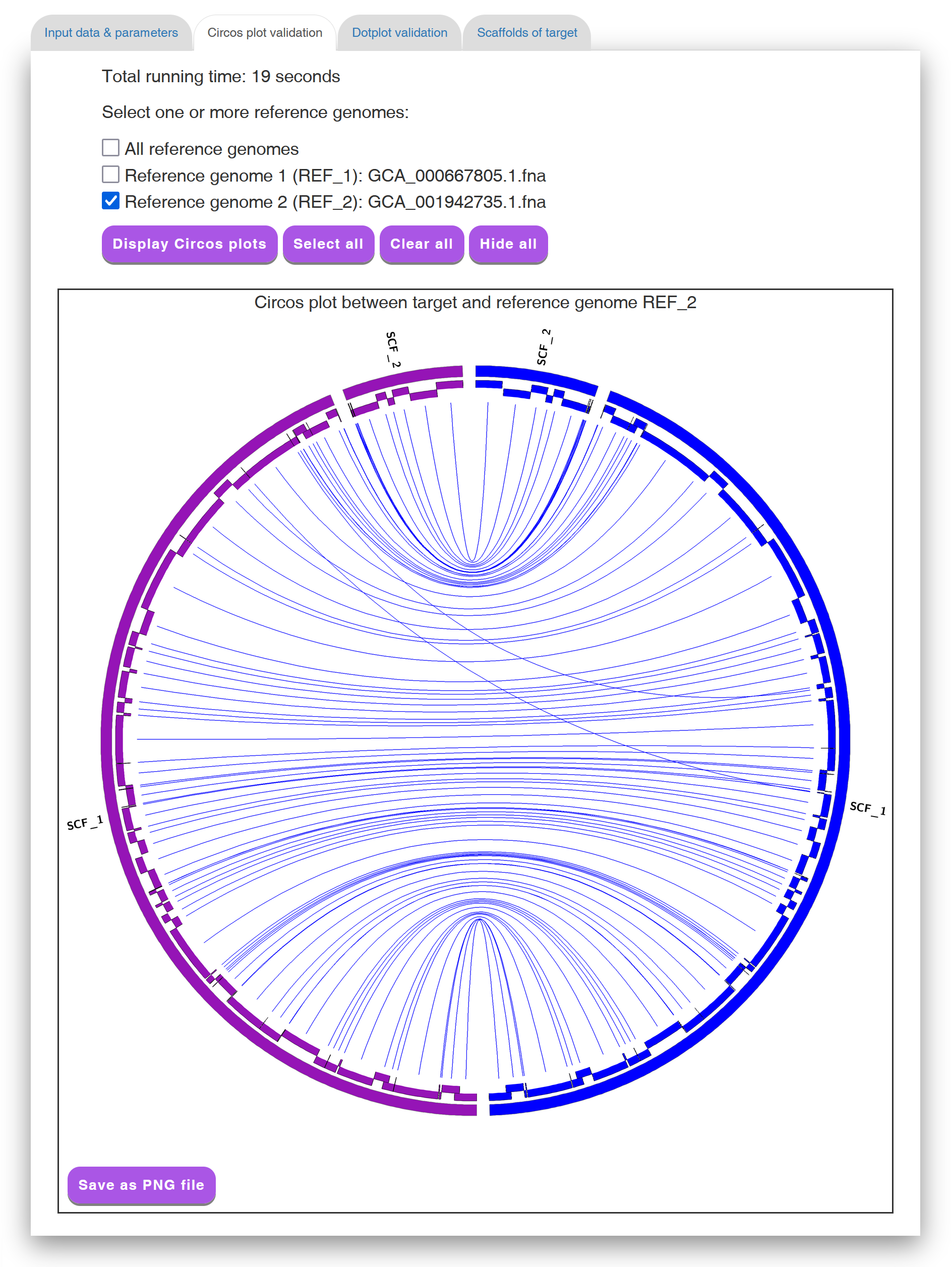
Figure 5: A display of a Circos plot between scaffolded target genome
and a selected reference genome, where the sequence markers are arranged
in alternating layers along the two-layer inner circle.
In the "Dotplot validation" tab page (see Figure 6 for an example), Multi-CSAR displays its its scaffolding result by a dotplot between the scaffolded target genome and a selected reference genome (the default is the first reference genome). If the contigs of the target genome are perfectly scaffolded according to the selected reference genome, the matched sequence regions of sequence markers in the dotplot would go from the bottom left to the top right (as shown in Figure 6) or go from the top left to the bottom right. Such a dotplot display of the scaffolding result is another convenient way to help the users to visually validate whether the contigs of the target genome are properly scaffolded according to the reference genomes.
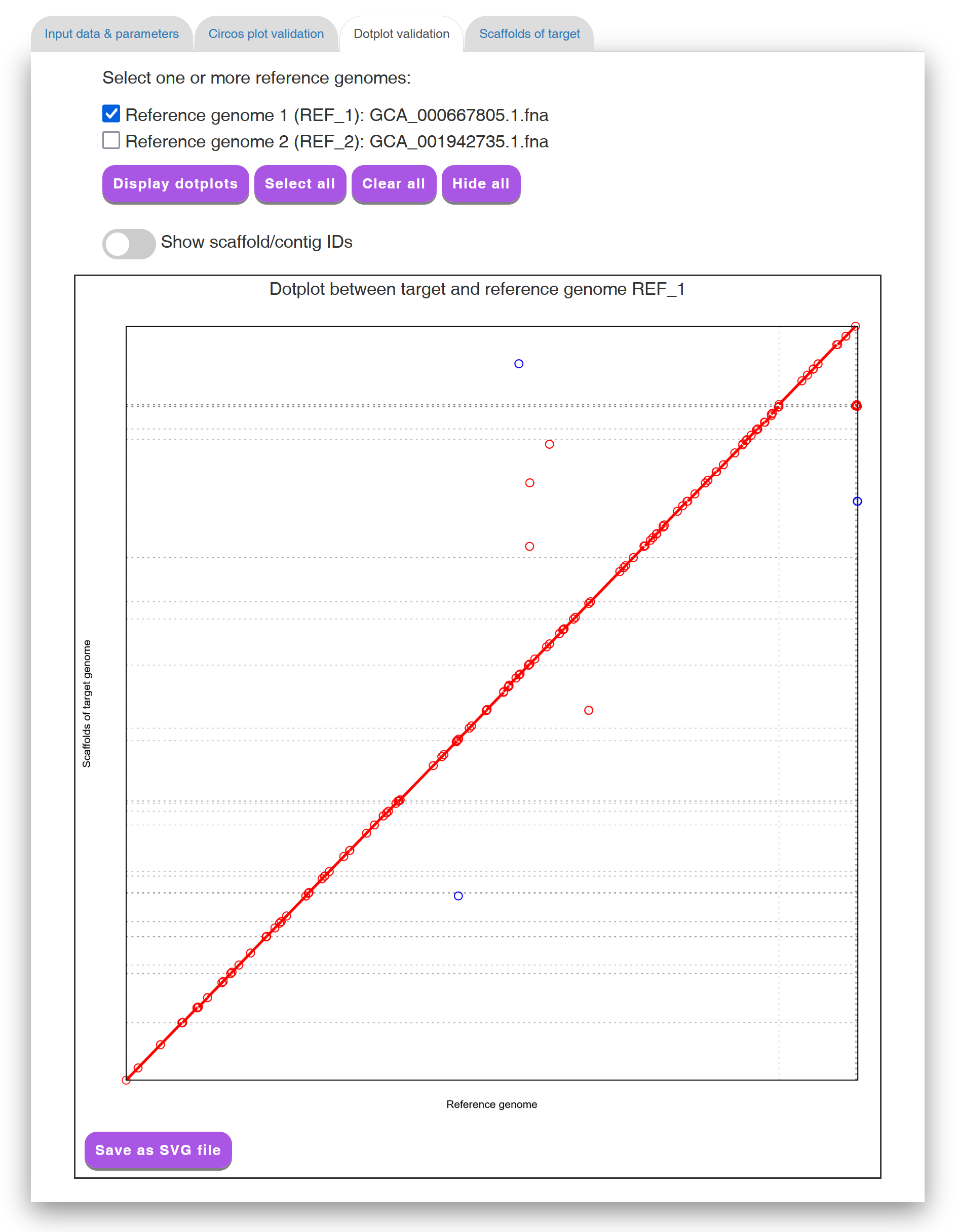
Figure 6: A display of the "Dotplot validation" tab page.
In the "Scaffolds of target" tab page. (see Figure 7 for an example), Multi-CSAR displays its scaffolding result in tabular format for the purpose of allowing the users to view the scaffolds of the target genome in detail. The scaffolds in the table are sorted according to their sizes, which equals to the sum of contig sizes. The contigs of each scaffold, along with their orientation (0 standing for forward and 1 for reverse), sequence and length, are listed in a table according to their order in the scaffold. For downstream analyses, the users can download the scaffolds of the target genome either in a tab-delimited text format or a comma-delimited CSV format by clicking the "Download scaffolds (.txt)" or "Download scaffolds (.csv)" button, respectively. In addition, the users can download the scaffold sequences in the text format by clicking the "Download sequences" button, where contig sequences in the same scaffold are separated by 100 Ns.